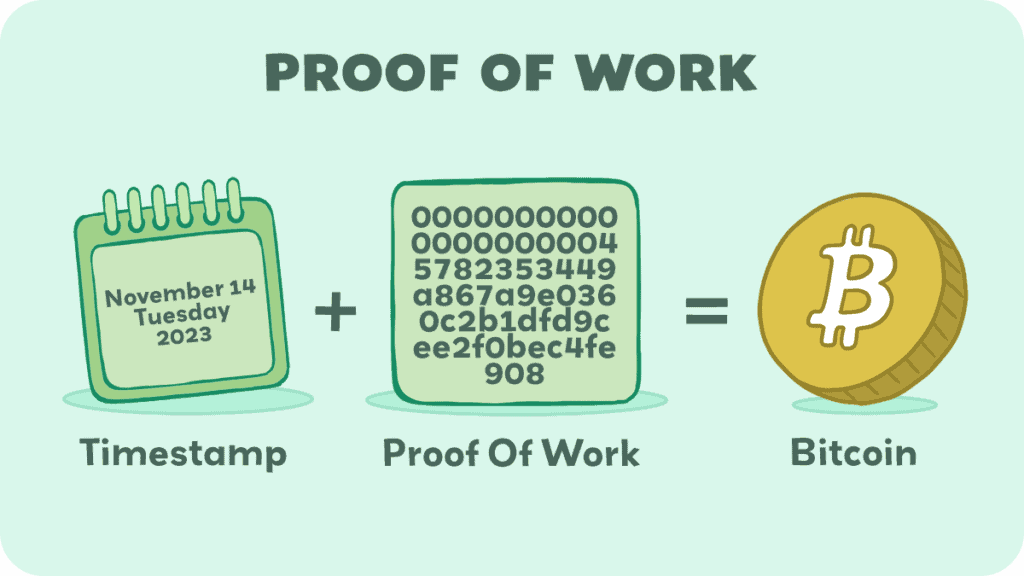
Proof of work (PoW) is a form of cryptographic proof in which one party proves to others that a certain amount of a specific computational effort has been expended commonly called a consensus mechanism.
It is provided by sending information in a block through a hash algorithm, and then adjusting the variable field until the hexadecimal number reaches the number that starts from a certain number of zeros which has a lower value than the network’s difficulty target.
This provides proof that the program expended the computational effort to hash the block until a solution is reached and the minor is provided with a reward.
How does “Proof of Work” work?
- The worker called a miner creates a temporary block. If it wins this competition to solve the hash to get the lowest number, this file is stored on the blockchain.
- The Block has the following fields:
- Block Size
- Block Header
- Transaction counter
- Transactions
- The Block has the following fields:
- The mining program assembles this block and places the transactions it has prioritized in the transaction field. It works as a ledger where everyone adds their transaction and to verify a transaction there are minier. It continuously adjusts the nonce and the extra nonce and sends the information in the block through a hashing algorithm
- It repeats the process until a solution is found, which has a value less than or equal to the difficulty target. The difficulty target is set so that a certain number of hashes per second must be attempted before a solution is found. The difficulty target dynamically adjusts based on the network hash rate to maintain the intended block time.
- example of a winning hash: 000000000000000000033028b3c8296ed776653032030cd01290f4345f5a9b6e
Consensus
After the block is closed and added to the chain, consensus on the feature most frequently linked to blockchain proofs is obtained. Each miner validates each new block as it is added while working on suggesting future blocks and creating winning hashes. Every miner notifies the network that the block it verified is legitimate.
By using the header hash of the preceding block, new blocks build a chain of proof that eventually results in network consensus. These proofs serve as the foundation for reaching consensus, which is why they are referred to as consensus procedures.
Key Features of PoW:
- Security: Because of the puzzle’s intricacy, attacking the network is costly and resource-intensive because it would require more processing power than the entire network.
- Decentralization: Anyone with the required technology and energy can mine, which contributes to the structure’s continued decentralization.
- Energy-Intensive: PoW uses a lot of energy since mining demands a lot of processing power.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
The proof of stake and proof of work are the two most widely used consensus techniques. Prior to its much-awaited switch to proof of stake in September 2022, Ethereum, the leading rival of Bitcoin, employed proof of work on its blockchain. The following are some of the main distinctions between the two.
Proof of Work
- A network of miners does the validation.
- Bitcoin paid for transaction fees and as a reward
- Being competitive requires a lot of effort and processing power.
Proof of Stake
- Participants who provide ether as collateral carry out validation.
- Ether is only used to cover transaction costs.
- Reduced energy and computing power usage
- Because there is little obstacle, consensus is formed more quickly.
Why Proof of Work is Important?
The foundation of today’s financial systems is trust. However, it has repeatedly been demonstrated that certain people are unreliable when it comes to financial matters. Since a proof is code, it eliminates the need to have faith that others are operating honorably. Code can take the place of our need to trust strangers if it is written with good intentions and cannot be changed since it is not enticed by money.
Conclusion
The development of the blockchain and cryptocurrency ecosystem has been greatly influenced by Proof of Work (PoW). By removing the need for trust in middlemen, its computational effort requirement guarantees safe, open, and decentralized networks. Over time, this consensus method has proven to be dependable by successfully preventing fraud and meddling with systems like Bitcoin.
PoW’s efficiency in delivering network security and decentralization is indisputable, despite its high energy consumption and environmental impact. Proof of Stake (PoW) is still a fundamental breakthrough, although alternatives like PoS provide more energy-efficient solutions.
PoW’s legacy will continue to shape the architecture of safe and untrustworthy systems as blockchain technology advances, highlighting its significance in the continuous advancement of decentralized technologies.
For more information visit: Investopedia